Biliopancreatic Diversion
Procedure: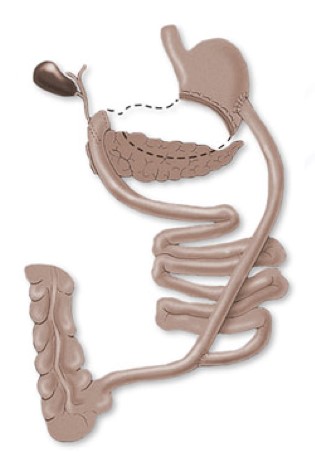
This procedure reduces the size of the stomach to 200-300 cc, resulting in a slight reduction of possible food intake. The degree of restriction depends on the size of the stomach left in place. In addition great parts of the small intestine are bypassed, resulting in a stronger malabsorption, especially for fat. The capacity to eat is greater than with the other operations, and the eventual weight loss is the best of all the operations but if fatty foods are overeaten e.g. a hamburger and fries then diarrhea and foul flatus will result.
Hospital stay: 2-3 days
Excessive weight loss: 70-90% in 2 years
Advantages of Biliopancreatic Diversion:
Besides a stable and rapid weight loss the Biliopancreatic diversion is well suited for patients with binge eating or sweet eating syndrome. Furthermore the procedure alters the blood sugar metabolism, leading to a diabetes remission in the majority of the patients (up to 95.1%).
Disadvantages of Biliopancreatic Diversion:
Owing to its malabsorptive effect life-long intake of vitamins and minerals (iron and calcium) are necessary as well as vitamin B12 injections every 6 months. A conventional upper gastroscopy of duodenum, remnant stomach and biliary tract is not possible after this type of surgery. Side effects include dumping syndrome, vertigo, flatulence and temporary discomfort. To prevent protein deficiency a protein-rich diet is important.
